Big Data Assignment - 2
Thejaswini L (4AD19CS094)
Big data technology is defined as software-utility. This technology is primarily designed to analyze, process and extract information from a large data set and a huge set of extremely complex structures. This is very difficult for traditional data processing software to deal with.
Among the larger concepts of rage in technology, big data technologies are widely associated with many other technologies such as deep learning, machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), and Internet of Things (IoT) that are massively augmented. In combination with these technologies, big data technologies are focused on analyzing and handling large amounts of real-time data and batch-related data.
Types of Big Data Technology
Operational Big Data Technologies
This type of big data technology mainly includes the basic day-to-day data that people used to process. Typically, the operational-big data includes daily basis data such as online transactions, social media platforms, and the data from any particular organization or a firm, which is usually needed for analysis using the software based on big data technologies. The data can also be referred to as raw data used as the input for several Analytical Big Data Technologies.
Some specific examples that include the Operational Big Data Technologies can be listed as below:
- Online ticket booking system, e.g., buses, trains, flights, and movies, etc.
- Online trading or shopping from e-commerce websites like Amazon, Flipkart, Walmart, etc.
- Online data on social media sites, such as Facebook, Instagram, Whatsapp, etc.
- The employees' data or executives' particulars in multinational companies.
Analytical Big Data Technologies
Analytical Big Data is commonly referred to as an improved version of Big Data Technologies. This type of big data technology is a bit complicated when compared with operational-big data. Analytical big data is mainly used when performance criteria are in use, and important real-time business decisions are made based on reports created by analyzing operational-real data. This means that the actual investigation of big data that is important for business decisions falls under this type of big data technology.
Some common examples that involve the Analytical Big Data Technologies can be listed as below:
- Stock marketing data
- Weather forecasting data and the time series analysis
- Medical health records where doctors can personally monitor the health status of an individual
- Carrying out the space mission databases where every information of a mission is very important
Top Big Data Technologies
We can categorize the leading big data technologies into the following four sections:
- Data Storage
- Data Mining
- Data Analytics
- Data Visualization
Data Storage
Let us first discuss leading Big Data Technologies that come under Data Storage:
- Hadoop: When it comes to handling big data, Hadoop is one of the leading technologies that come into play. This technology is based entirely on map-reduce architecture and is mainly used to process batch information. Also, it is capable enough to process tasks in batches. The Hadoop framework was mainly introduced to store and process data in a distributed data processing environment parallel to commodity hardware and a basic programming execution model.
Apart from this, Hadoop is also best suited for storing and analyzing the data from various machines with a faster speed and low cost. That is why Hadoop is known as one of the core components of big data technologies. The Apache Software Foundation introduced it in Dec 2011. Hadoop is written in Java programming language. - MongoDB: MongoDB is another important component of big data technologies in terms of storage. No relational properties and RDBMS properties apply to MongoDb because it is a NoSQL database. This is not the same as traditional RDBMS databases that use structured query languages. Instead, MongoDB uses schema documents.
The structure of the data storage in MongoDB is also different from traditional RDBMS databases. This enables MongoDB to hold massive amounts of data. It is based on a simple cross-platform document-oriented design. The database in MongoDB uses documents similar to JSON with the schema. This ultimately helps operational data storage options, which can be seen in most financial organizations. As a result, MongoDB is replacing traditional mainframes and offering the flexibility to handle a wide range of high-volume data-types in distributed architectures.
MongoDB Inc. introduced MongoDB in Feb 2009. It is written with a combination of C++, Python, JavaScript, and Go language. - RainStor: RainStor is a popular database management system designed to manage and analyze organizations' Big Data requirements. It uses deduplication strategies that help manage storing and handling vast amounts of data for reference.
RainStor was designed in 2004 by a RainStor Software Company. It operates just like SQL. Companies such as Barclays and Credit Suisse are using RainStor for their big data needs. - Hunk: Hunk is mainly helpful when data needs to be accessed in remote Hadoop clusters using virtual indexes. This helps us to use the spunk search processing language to analyze data. Also, Hunk allows us to report and visualize vast amounts of data from Hadoop and NoSQL data sources.
Hunk was introduced in 2013 by Splunk Inc. It is based on the Java programming language. - Cassandra: Cassandra is one of the leading big data technologies among the list of top NoSQL databases. It is open-source, distributed and has extensive column storage options. It is freely available and provides high availability without fail. This ultimately helps in the process of handling data efficiently on large commodity groups. Cassandra's essential features include fault-tolerant mechanisms, scalability, MapReduce support, distributed nature, eventual consistency, query language property, tunable consistency, and multi-datacenter replication, etc.
Cassandra was developed in 2008 by the Apache Software Foundation for the Facebook inbox search feature. It is based on the Java programming language.
Data Mining
- Presto: Presto is an open-source and a distributed SQL query engine developed to run interactive analytical queries against huge-sized data sources. The size of data sources can vary from gigabytes to petabytes. Presto helps in querying the data in Cassandra, Hive, relational databases and proprietary data storage systems.
Presto is a Java-based query engine that was developed in 2013 by the Apache Software Foundation. Companies like Repro, Netflix, Airbnb, Facebook and Checkr are using this big data technology and making good use of it. - RapidMiner: RapidMiner is defined as the data science software that offers us a very robust and powerful graphical user interface to create, deliver, manage, and maintain predictive analytics. Using RapidMiner, we can create advanced workflows and scripting support in a variety of programming languages.
RapidMiner is a Java-based centralized solution developed in 2001 by Ralf Klinkenberg, Ingo Mierswa, and Simon Fischer at the Technical University of Dortmund's AI unit. It was initially named YALE (Yet Another Learning Environment). A few sets of companies that are making good use of the RapidMiner tool are Boston Consulting Group, InFocus, Domino's, Slalom, and Vivint.SmartHome. - ElasticSearch: When it comes to finding information, elasticsearch is known as an essential tool. It typically combines the main components of the ELK stack (i.e., Logstash and Kibana). In simple words, ElasticSearch is a search engine based on the Lucene library and works similarly to Solr. Also, it provides a purely distributed, multi-tenant capable search engine. This search engine is completely text-based and contains schema-free JSON documents with an HTTP web interface.
ElasticSearch is primarily written in a Java programming language and was developed in 2010 by Shay Banon. Now, it has been handled by Elastic NV since 2012. ElasticSearch is used by many top companies, such as LinkedIn, Netflix, Facebook, Google, Accenture, StackOverflow, etc.
Data Analytics
Now, let us discuss leading Big Data Technologies that come under Data Analytics:
- Apache Kafka: Apache Kafka is a popular streaming platform. This streaming platform is primarily known for its three core capabilities: publisher, subscriber and consumer. It is referred to as a distributed streaming platform. It is also defined as a direct messaging, asynchronous messaging broker system that can ingest and perform data processing on real-time streaming data. This platform is almost similar to an enterprise messaging system or messaging queue.
Besides, Kafka also provides a retention period, and data can be transmitted through a producer-consumer mechanism. Kafka has received many enhancements to date and includes some additional levels or properties, such as schema, Ktables, KSql, registry, etc. It is written in Java language and was developed by the Apache software community in 2011. Some top companies using the Apache Kafka platform include Twitter, Spotify, Netflix, Yahoo, LinkedIn etc. - Splunk: Splunk is known as one of the popular software platforms for capturing, correlating, and indexing real-time streaming data in searchable repositories. Splunk can also produce graphs, alerts, summarized reports, data visualizations, and dashboards, etc., using related data. It is mainly beneficial for generating business insights and web analytics. Besides, Splunk is also used for security purposes, compliance, application management and control.
Splunk Inc. introduced Splunk in the year 2014. It is written in combination with AJAX, Python, C ++ and XML. Companies such as Trustwave, QRadar, and 1Labs are making good use of Splunk for their analytical and security needs. - KNIME: KNIME is used to draw visual data flows, execute specific steps and analyze the obtained models, results, and interactive views. It also allows us to execute all the analysis steps altogether. It consists of an extension mechanism that can add more plugins, giving additional features and functionalities.
KNIME is based on Eclipse and written in a Java programming language. It was developed in 2008 by KNIME Company. A list of companies that are making use of KNIME includes Harnham, Tyler, and Paloalto. - Spark: Apache Spark is one of the core technologies in the list of big data technologies. It is one of those essential technologies which are widely used by top companies. Spark is known for offering In-memory computing capabilities that help enhance the overall speed of the operational process. It also provides a generalized execution model to support more applications. Besides, it includes top-level APIs (e.g., Java, Scala, and Python) to ease the development process.
Also, Spark allows users to process and handle real-time streaming data using batching and windowing operations techniques. This ultimately helps to generate datasets and data frames on top of RDDs. As a result, the integral components of Spark Core are produced. Components like Spark MlLib, GraphX, and R help analyze and process machine learning and data science. Spark is written using Java, Scala, Python and R language. The Apache Software Foundation developed it in 2009. Companies like Amazon, ORACLE, CISCO, VerizonWireless, and Hortonworks are using this big data technology and making good use of it. - R-Language: R is defined as the programming language, mainly used in statistical computing and graphics. It is a free software environment used by leading data miners, practitioners and statisticians. Language is primarily beneficial in the development of statistical-based software and data analytics.
R-language was introduced in Feb 2000 by R-Foundation. It is written in Fortran. Companies like Barclays, American Express, and Bank of America use R-Language for their data analytics needs. - Blockchain: Blockchain is a technology that can be used in several applications related to different industries, such as finance, supply chain, manufacturing, etc. It is primarily used in processing operations like payments and escrow. This helps in reducing the risks of fraud. Besides, it enhances the transaction's overall processing speed, increases financial privacy, and internationalize the markets. Additionally, it is also used to fulfill the needs of shared ledger, smart contract, privacy, and consensus in any Business Network Environment.
Blockchain technology was first introduced in 1991 by two researchers, Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta. However, blockchain has its first real-world application in Jan 2009 when Bitcoin was launched. It is a specific type of database based on Python, C++, and JavaScript. ORACLE, Facebook, and MetLife are a few of those top companies using Blockchain technology.
Data Visualization
Let us discuss leading Big Data Technologies that come under Data Visualization:
- Tableau: Tableau is one of the fastest and most powerful data visualization tools used by leading business intelligence industries. It helps in analyzing the data at a very faster speed. Tableau helps in creating the visualizations and insights in the form of dashboards and worksheets.
Tableau is developed and maintained by a company named TableAU. It was introduced in May 2013. It is written using multiple languages, such as Python, C, C++, and Java. Some of the list's top companies are Cognos, QlikQ, and ORACLE Hyperion, using this tool. - Plotly: As the name suggests, Plotly is best suited for plotting or creating graphs and relevant components at a faster speed in an efficient way. It consists of several rich libraries and APIs, such as MATLAB, Python, Julia, REST API, Arduino, R, Node.js, etc. This helps interactive styling graphs with Jupyter notebook and Pycharm.
Plotly was introduced in 2012 by Plotly company. It is based on JavaScript. Paladins and Bitbank are some of those companies that are making good use of Plotly.
Emerging Big Data Technologies
Apart from the above mentioned big data technologies, there are several other emerging big data technologies. The following are some essential technologies among them:
- TensorFlow: TensorFlow combines multiple comprehensive libraries, flexible ecosystem tools, and community resources that help researchers implement the state-of-art in Machine Learning. Besides, this ultimately allows developers to build and deploy machine learning-powered applications in specific environments.
TensorFlow was introduced in 2019 by Google Brain Team. It is mainly based on C++, CUDA, and Python. Companies like Google, eBay, Intel, and Airbnb are using this technology for their business requirements. - Beam: Apache Beam consists of a portable API layer that helps build and maintain sophisticated parallel-data processing pipelines. Apart from this, it also allows the execution of built pipelines across a diversity of execution engines or runners.
Apache Beam was introduced in June 2016 by the Apache Software Foundation. It is written in Python and Java. Some leading companies like Amazon, ORACLE, Cisco, and VerizonWireless are using this technology. - Docker: Docker is defined as the special tool purposely developed to create, deploy, and execute applications easier by using containers. Containers usually help developers pack up applications properly, including all the required components like libraries and dependencies. Typically, containers bind all components and ship them all together as a package.
Docker was introduced in March 2003 by Docker Inc. It is based on the Go language. Companies like Business Insider, Quora, Paypal, and Splunk are using this technology. - Airflow: Airflow is a technology that is defined as a workflow automation and scheduling system. This technology is mainly used to control, and maintain data pipelines. It contains workflows designed using the DAGs (Directed Acyclic Graphs) mechanism and consisting of different tasks. The developers can also define workflows in codes that help in easy testing, maintenance, and versioning.
Airflow was introduced in May 2019 by the Apache Software Foundation. It is based on a Python language. Companies like Checkr and Airbnb are using this leading technology. - Kubernetes: Kubernetes is defined as a vendor-agnostic cluster and container management tool made open-source in 2014 by Google. It provides a platform for automation, deployment, scaling, and application container operations in the host clusters.
Kubernetes was introduced in July 2015 by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation. It is written in the Go language. Companies like American Express, Pear Deck, PeopleSource, and Northwestern Mutual are making good use of this technology.
These are emerging technologies. However, they are not limited because the ecosystem of big data is constantly emerging. That is why new technologies are coming at a very fast pace based on the demand and requirements of IT industries.
What is Hadoop?
Hadoop is an open source framework from Apache and is used to store process and analyze data which are very huge in volume. Hadoop is written in Java and is not OLAP (online analytical processing). It is used for batch/offline processing.It is being used by Facebook, Yahoo, Google, Twitter, LinkedIn and many more. Moreover it can be scaled up just by adding nodes in the cluster.
Modules of Hadoop
- HDFS: Hadoop Distributed File System. Google published its paper GFS and on the basis of that HDFS was developed. It states that the files will be broken into blocks and stored in nodes over the distributed architecture.
- Yarn: Yet another Resource Negotiator is used for job scheduling and manage the cluster.
- Map Reduce: This is a framework which helps Java programs to do the parallel computation on data using key value pair. The Map task takes input data and converts it into a data set which can be computed in Key value pair. The output of Map task is consumed by reduce task and then the out of reducer gives the desired result.
- Hadoop Common: These Java libraries are used to start Hadoop and are used by other Hadoop modules.
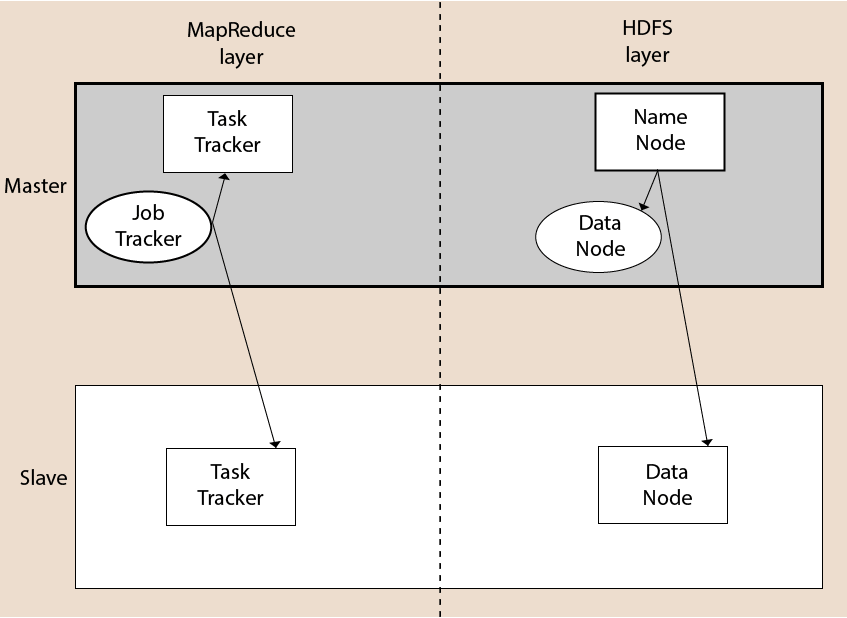
Hadoop Architecture
The Hadoop architecture is a package of the file system, MapReduce engine and the HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System). The MapReduce engine can be MapReduce/MR1 or YARN/MR2.
A Hadoop cluster consists of a single master and multiple slave nodes. The master node includes Job Tracker, Task Tracker, NameNode, and DataNode whereas the slave node includes DataNode and TaskTracker.
Hadoop Installation
Environment required for Hadoop: The production environment of Hadoop is UNIX, but it can also be used in Windows using Cygwin. Java 1.6 or above is needed to run Map Reduce Programs. For Hadoop installation from tar ball on the UNIX environment you need
- Java Installation
- SSH installation
- Hadoop Installation and File Configuration
Hadoop Distributed File System
The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) is a distributed file system for Hadoop. It contains a master/slave architecture. This architecture consist of a single NameNode performs the role of master, and multiple DataNodes performs the role of a slave.
Both NameNode and DataNode are capable enough to run on commodity machines. The Java language is used to develop HDFS. So any machine that supports Java language can easily run the NameNode and DataNode software.
NameNode
- It is a single master server exist in the HDFS cluster.
- As it is a single node, it may become the reason of single point failure.
- It manages the file system namespace by executing an operation like the opening, renaming and closing the files.
- It simplifies the architecture of the system.
DataNode
- The HDFS cluster contains multiple DataNodes.
- Each DataNode contains multiple data blocks.
- These data blocks are used to store data.
- It is the responsibility of DataNode to read and write requests from the file system's clients.
- It performs block creation, deletion, and replication upon instruction from the NameNode.
Job Tracker
- The role of Job Tracker is to accept the MapReduce jobs from client and process the data by using NameNode.
- In response, NameNode provides metadata to Job Tracker.
Task Tracker
- It works as a slave node for Job Tracker.
- It receives task and code from Job Tracker and applies that code on the file. This process can also be called as a Mapper.
MapReduce Layer
The MapReduce comes into existence when the client application submits the MapReduce job to Job Tracker. In response, the Job Tracker sends the request to the appropriate Task Trackers. Sometimes, the TaskTracker fails or time out. In such a case, that part of the job is rescheduled.
Advantages of Hadoop
- Fast: In HDFS the data distributed over the cluster and are mapped which helps in faster retrieval. Even the tools to process the data are often on the same servers, thus reducing the processing time. It is able to process terabytes of data in minutes and Peta bytes in hours.
- Scalable: Hadoop cluster can be extended by just adding nodes in the cluster.
- Cost Effective: Hadoop is open source and uses commodity hardware to store data so it really cost effective as compared to traditional relational database management system.
- Resilient to failure: HDFS has the property with which it can replicate data over the network, so if one node is down or some other network failure happens, then Hadoop takes the other copy of data and use it. Normally, data are replicated thrice but the replication factor is configurable.
History of Hadoop
The Hadoop was started by Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella in 2002. Its origin was the Google File System paper, published by Google.
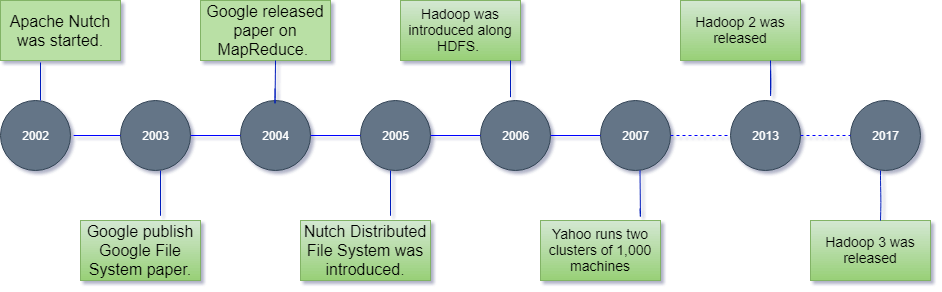
Let's focus on the history of Hadoop in the following steps: -
- In 2002, Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella started to work on a project, Apache Nutch. It is an open source web crawler software project.
- While working on Apache Nutch, they were dealing with big data. To store that data they have to spend a lot of costs which becomes the consequence of that project. This problem becomes one of the important reason for the emergence of Hadoop.
- In 2003, Google introduced a file system known as GFS (Google file system). It is a proprietary distributed file system developed to provide efficient access to data.
- In 2004, Google released a white paper on Map Reduce. This technique simplifies the data processing on large clusters.
- In 2005, Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella introduced a new file system known as NDFS (Nutch Distributed File System). This file system also includes Map reduce.
- In 2006, Doug Cutting quit Google and joined Yahoo. On the basis of the Nutch project, Dough Cutting introduces a new project Hadoop with a file system known as HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System). Hadoop first version 0.1.0 released in this year.
- Doug Cutting gave named his project Hadoop after his son's toy elephant.
- In 2007, Yahoo runs two clusters of 1000 machines.
- In 2008, Hadoop became the fastest system to sort 1 terabyte of data on a 900 node cluster within 209 seconds.
- In 2013, Hadoop 2.2 was released.
- In 2017, Hadoop 3.0 was released.
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 2003 | Google released the paper, Google File System (GFS). |
| 2004 | Google released a white paper on Map Reduce. |
| 2006 |
|
| 2007 |
|
| 2008 |
|
| 2009 |
|
| 2010 |
|
| 2011 |
|
| 2012 | Apache Hadoop 1.0 version released. |
| 2013 | Apache Hadoop 2.2 version released. |
| 2014 | Apache Hadoop 2.6 version released. |
| 2015 | Apache Hadoop 2.7 version released. |
| 2017 | Apache Hadoop 3.0 version released. |
| 2018 | Apache Hadoop 3.1 version released. |
What is MongoDB?
MongoDB is an open-source document database that provides high performance, high availability, and automatic scaling.
In simple words, you can say that - Mongo DB is a document-oriented database. It is an open source product, developed and supported by a company named 10gen.
MongoDB is available under General Public license for free, and it is also available under Commercial license from the manufacturer.
The manufacturing company 10gen has defined MongoDB as:
"MongoDB is a scalable, open source, high performance, document-oriented database." - 10gen
MongoDB was designed to work with commodity servers. Now it is used by the company of all sizes, across all industry.
History of MongoDB
The initial development of MongoDB began in 2007 when the company was building a platform as a service similar to window azure.
Window azure is a cloud computing platform and infrastructure, created by Microsoft, to build, deploy and manage applications and service through a global network.
MongoDB was developed by a NewYork based organization named 10gen which is now known as MongoDB Inc. It was initially developed as a PAAS (Platform as a Service). Later in 2009, it is introduced in the market as an open source database server that was maintained and supported by MongoDB Inc.
The first ready production of MongoDB has been considered from version 1.4 which was released in March 2010.
Purpose of Building MongoDB
It may be a very genuine question that - "what was the need of MongoDB although there were many databases in action?"
There is a simple answer:
All the modern applications require big data, fast features development, flexible deployment, and the older database systems not competent enough, so the MongoDB was needed.
The primary purpose of building MongoDB is:
- Scalability
- Performance
- High Availability
- Scaling from single server deployments to large, complex multi-site architectures.
- Key points of MongoDB
- Develop Faster
- Deploy Easier
- Scale Bigger
Example of Document-Oriented Database
MongoDB is a document-oriented database. It is a key feature of MongoDB. It offers a document-oriented storage. It is very simple you can program it easily.
MongoDB stores data as documents, so it is known as document-oriented database.
There are two different documents (separated by ".").
Storing data in this manner is called as document-oriented database.
Mongo DB falls into a class of databases that calls Document Oriented Databases. There is also a broad category of database known as No SQL Databases.
Features of MongoDB
These are some important features of MongoDB:
1. Support ad hoc queries
In MongoDB, you can search by field, range query and it also supports regular expression searches.
2. Indexing
You can index any field in a document.
3. Replication
MongoDB supports Master Slave replication.
A master can perform Reads and Writes and a Slave copies data from the master and can only be used for reads or back up (not writes)
4. Duplication of data
MongoDB can run over multiple servers. The data is duplicated to keep the system up and also keep its running condition in case of hardware failure.
5. Load balancing
It has an automatic load balancing configuration because of data placed in shards.
6. Supports map reduce and aggregation tools.
7. Uses JavaScript instead of Procedures.
8. It is a schema-less database written in C++.
9. Provides high performance.
10. Stores files of any size easily without complicating your stack.
11. Easy to administer in the case of failures.
12. It also supports:
- JSON data model with dynamic schemas
- Auto-sharding for horizontal scalability
- Built in replication for high availability
- Now a day many companies using MongoDB to create new types of applications, improve performance and availability.
MongoDB Advantages
- MongoDB is schema less. It is a document database in which one collection holds different documents.
- There may be difference between number of fields, content and size of the document from one to other.
- Structure of a single object is clear in MongoDB.
- There are no complex joins in MongoDB.
- MongoDB provides the facility of deep query because it supports a powerful dynamic query on documents.
- It is very easy to scale.
- It uses internal memory for storing working sets and this is the reason of its fast access.
Distinctive features of MongoDB
- Easy to use
- Light Weight
- Extremely faster than RDBMS
Where MongoDB should be used
- Big and complex data
- Mobile and social infrastructure
- Content management and delivery
- User data management
- Data hub
Language Support by MongoDB:
MongoDB currently provides official driver support for all popular programming languages like C, C++, Rust, C#, Java, Node.js, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, Scala, Go, and Erlang.
Installing MongoDB:
Just go to http://www.mongodb.org/downloads and select your operating system out of Windows, Linux, Mac OS X and Solaris. A detailed explanation about the installation of MongoDB is given on their site.
.png)



Comments
Post a Comment